
Plant stomata, LM Stock Image C036/0609 Science Photo Library
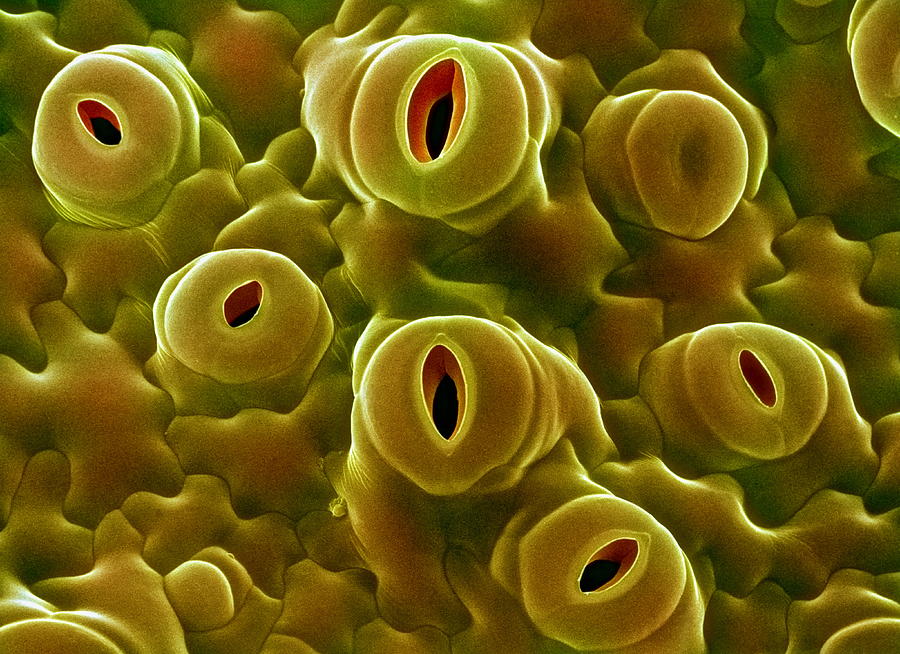
Stoma Stoma in a tomato leaf shown via colorized scanning electron microscope image A stoma in horizontal cross section The underside of a leaf. In this species ( Tradescantia zebrina) the guard cells of the stomata are green because they contain chlorophyll while the epidermal cells are chlorophyll-free and contain red pigments.
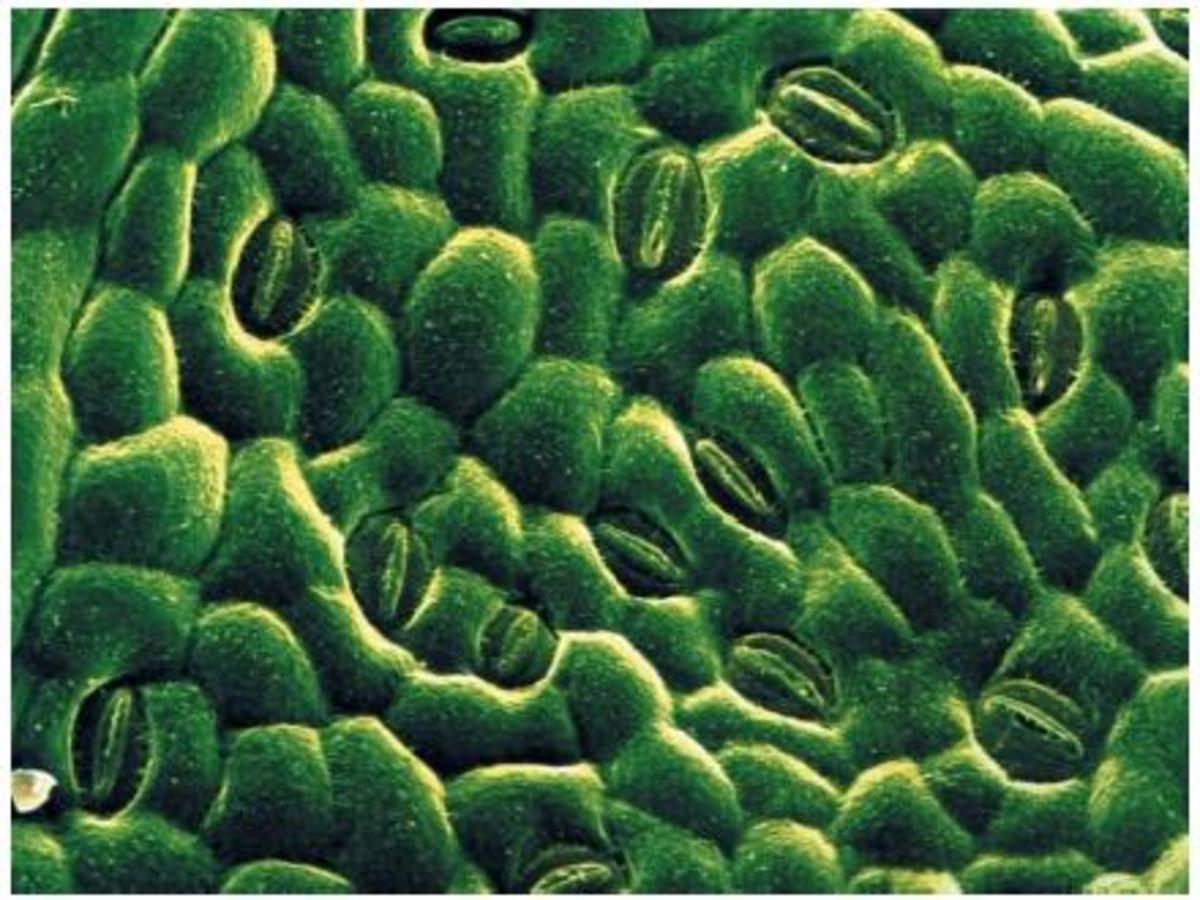
The Crucial Role of Stomata in Plant Transpiration and Photosynthesis HubPages
The stomata are minute pores or openings found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other plant organs that allow gases such as carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water vapor to diffuse into and out of the internal tissues of the plant. Stomata is the plural form of the stoma. In greek, stoma means "mouth".
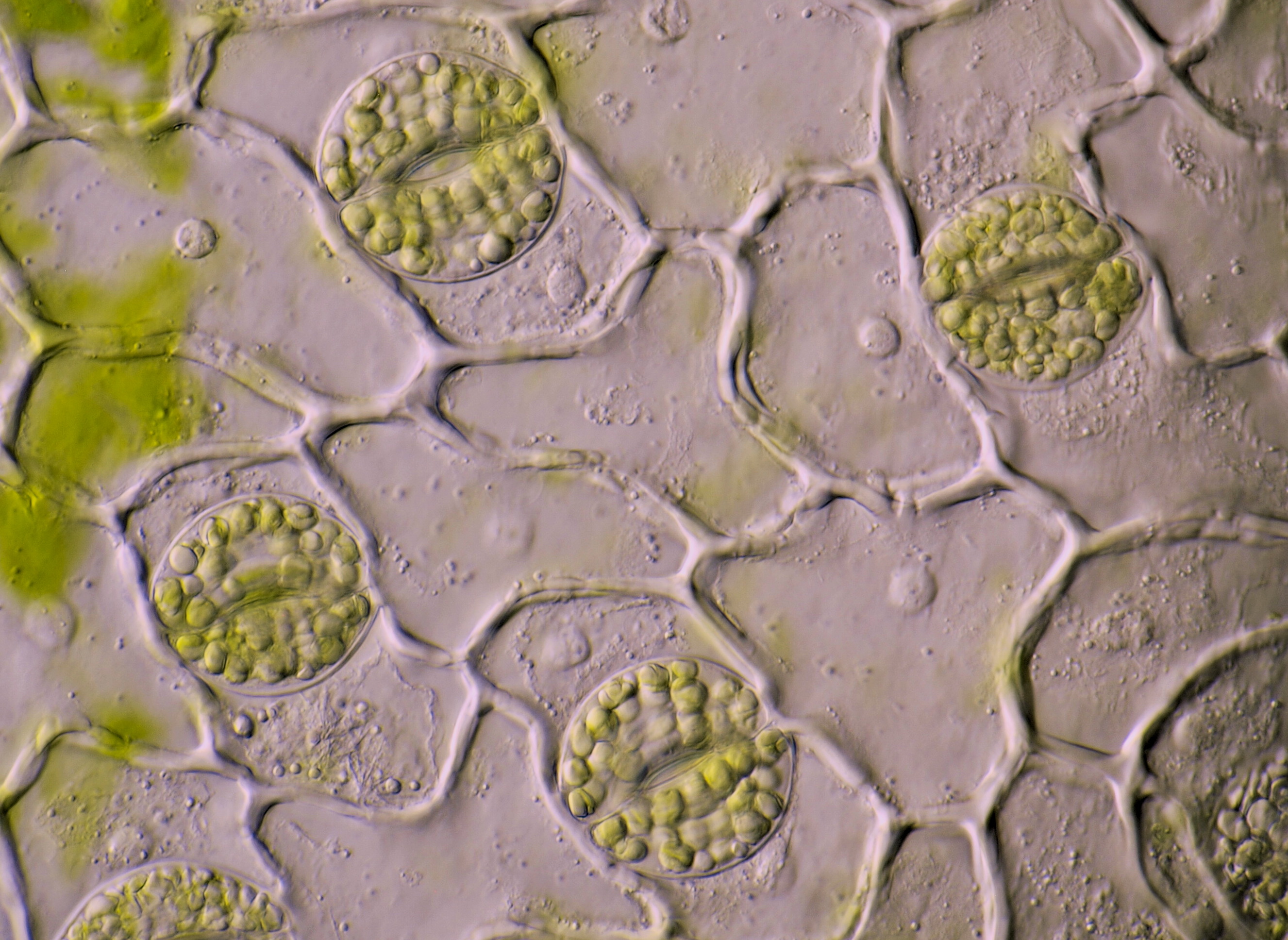
Stomata Microscopy of Nature
Browse 1,400+ stomata leaf stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. Stoma. Close-up of a pore in the epidermis of leaves. Stoma. Close-up of a pore in the epidermis of leaves, and stems for gas exchange. Magnified leaf stomata.

116 Homeostasis in plants Biology Notes for A level
These images of Tradescantia zebrina stomata belong to the first photos I ever took of this plant. At that time, as a camera I still used the Olympus Stylus 725 SW, a simple compact camera. Objective: Carl Zeiss 100/1.25. If you look at an intact leaf of Tradescantia zebrina through the microscope, a special picture emerges. The leaves of this.
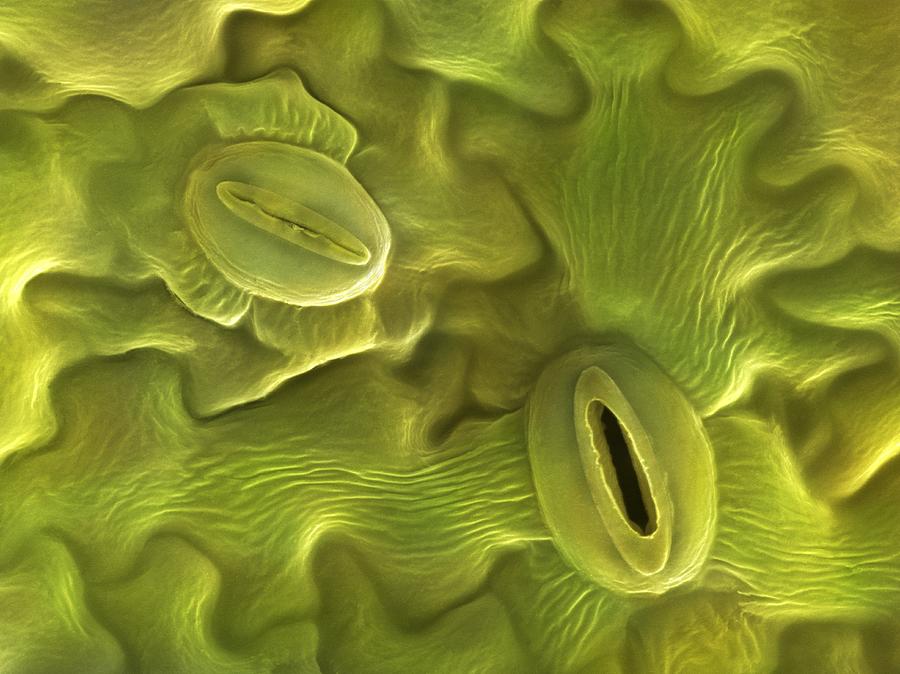
Stomata Of Lavendula Dentata, Sem Photograph by Power And Syred
Stomata (singular stoma) are tiny openings or pores found in the epidermis of leaves and young stems that helps in gas exchange. Pair of specialized bean-shaped cells called guard cells are found to surround each stoma. Just like animals breathe, plants do so with the help of stomata. Under the microscope, they appear dense or dark.

The Importance of Stomata Plant Physiology
stomate, any of the microscopic openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems. Stomata are generally more numerous on the underside of leaves. They provide for the exchange of gases between the outside air and the branched system of interconnecting air canals within the leaf. stoma with guard cells

Stomata Structure, Types and Functions Plantlet Anatomy Plantlet
Stomata in plants appear as minute pores, primarily in the epidermis layer of the leaf surface and rarely in some of the herbaceous stems. It was originated from the Greek word stoma (means mouth) to relate it with the term "stomatal pore".A stoma is a singular form, whereas a high number of stoma is termed stomata (a plural form).
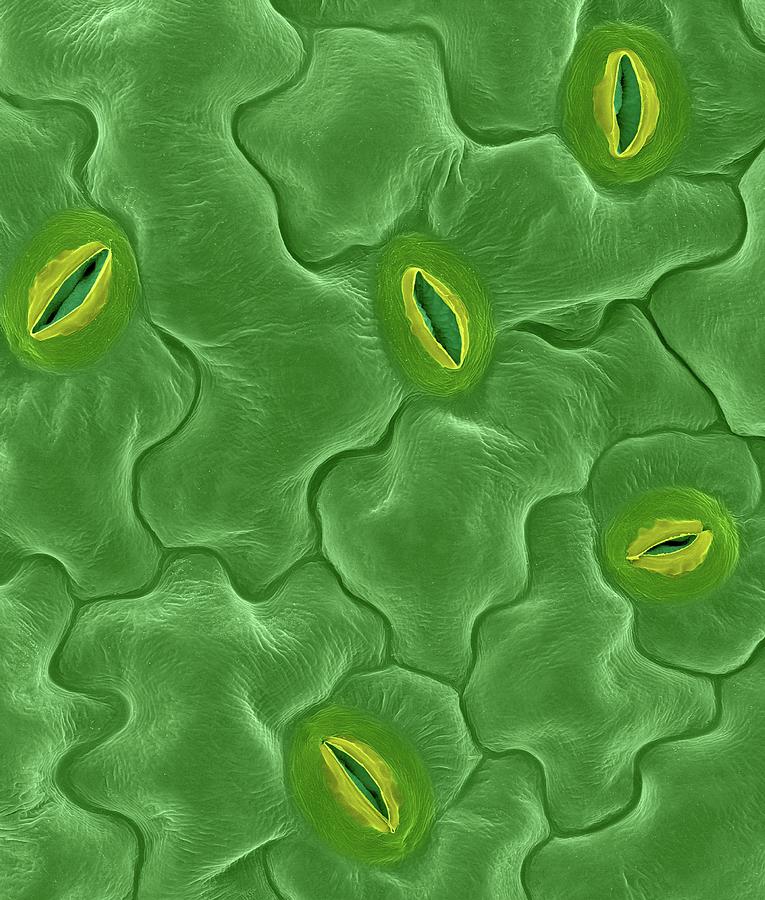
Leaf Stomata (arabidopsis Sp.) Photograph by Dennis Kunkel Microscopy/science Photo Library Pixels
Stomata can be distributed in the following ways on the two sides of a leaf: • An amphistomatous leaf has stomata on both surfaces. Most plants have such a distribution. • A hypostomatous leaf has stomata only on the lower surface. Many tree species are characterized by having hypostomatous leaves, such as horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) and basswood (Tilia europaea) (Meidner and.

Stomate Definition, Function, Description, Structure, & Importance Britannica
Stomata (singular, "stoma") are tiny pores through which plants breathe. Stomata are found on the upper and lower sides of leaves, on flower petals, on stems, and on roots.

Stomata in Plants Definition, Purpose & Types Video & Lesson Transcript
What are Stomata? Stomata are the tiny openings present on the epidermis of leaves. We can see stomata under the light microscope. In some of the plants, stomata are present on stems and other parts of plants. Stomata play an important role in gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. They control by transpiration rate by opening and closing.
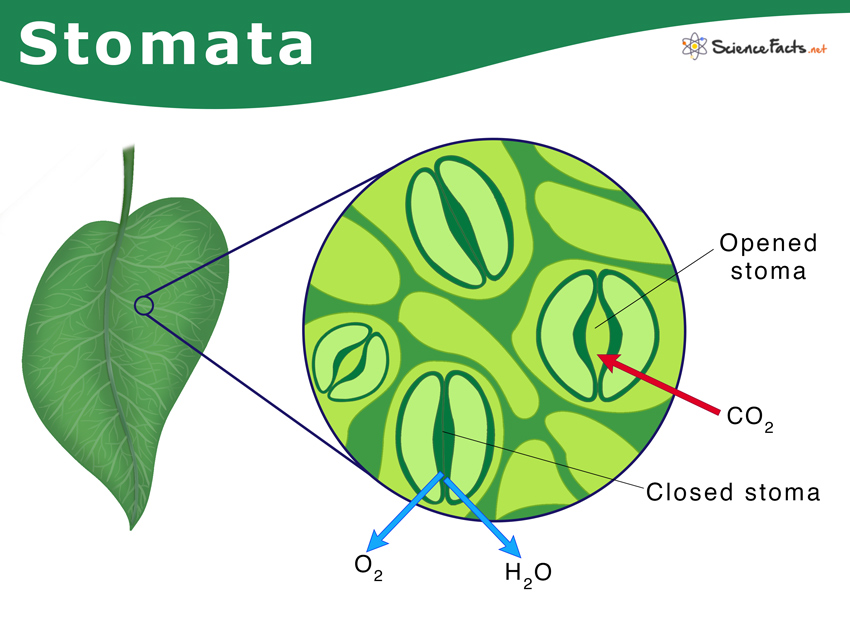
Stomata Definition, Types, Structure, & Function
1,734 stomata stock photos, 3D objects, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See stomata stock video clips Filters All images Photos Vectors Illustrations 3D Objects Sort by Popular Magnified leaf stomata - schematic (opened and closed) Leaf stomata under the microscope Diagram showing schematic stomata illustration

Stomate Definition, Function, Description, Structure, & Importance Britannica
Stomata is the tiny pores found in the epidermis of leaves and other organs. Learn more about the Diagram Of Stomata along with their labellings at BYJU'S

June 2015 PLANT STOMATA ENCYCLOPEDIA
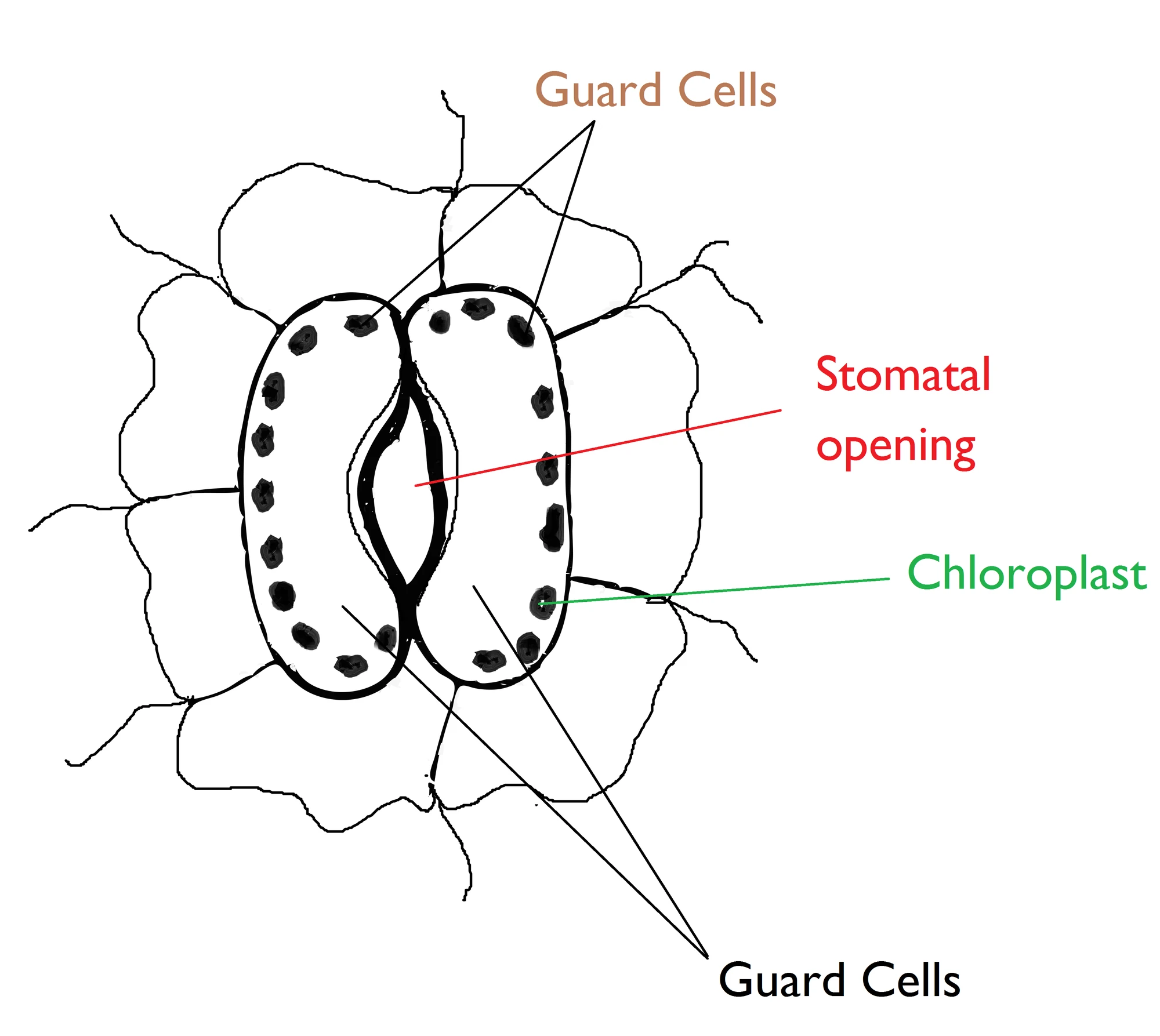
Definition of Stomata: The stomata are minute pores which occur in the epidermis of the plants. Each stoma remains surrounded by two kidneys or bean shaped epidermal cells the guard cells. The stomata may occur on any part of a plant except the roots. The epidermal cells bordering the guard cells are called accessory cells or subsidiary cells.
Stomata Allows movement of gases in and out of the inter cellular spaces. SThompson4th2014
Figure 4.5.1.2.2.1 4.5.1.2.2. 1: Italian chicory leaf epidermis showing stomata. The epidermal cells are shaped like puzzle pieces. The stomata (singular = stoma) are pores in the epidermis. Each is bordered by two guard cells, which are filled with oval, green chloroplasts. Image by Umberto Salvagnin ( CC-BY ).
Stomata Open Science Wiki Fandom
Find the perfect stomata stock photo, image, vector, illustration or 360 image. Available for both RF and RM licensing. Images. Images homepage. Photos. Vectors.. Search Results for Stomata Stock Photos and Images (2,228) Page 1 of 23. Go to page. Stock photos, 360° images, vectors and videos. Changing the world one image at a time. English.

Stomata Structure, Diagram, Types & Functions Embibe
Stoma Definition. In plants, a stoma is a tiny pore in the surface of a leaf that is used for gas exchange. Most leaves are covered in these tiny pores, which allow the plants to take in carbon dioxide for use in photosynthesis and expel their waste oxygen. The term "stoma" comes from the Greek word for "mouth.".